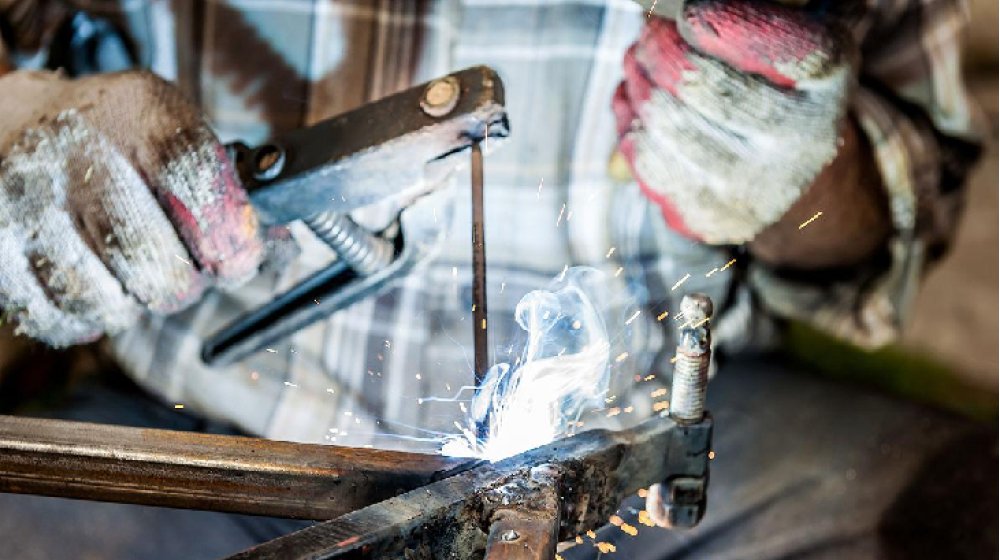
Fume Extraction System in Welding School
Welding fumes are a hazardous mix of manganese, hexavalent chromium, and other toxic substances linked to asthma, metal-fume fever, and chronic neurological disorders. A dedicated fume extraction system for welding school settings captures these dangerous particles directly at the source—preventing inhalation by students and contamination of costly equipment. Beyond safeguarding health, a properly designed system ensures compliance with OSHA, EPA, and fire safety regulations.
Welding Training Center: Key Characteristics
Welding schools train students and beginners in fundamental techniques. The workpieces are typically small and stationary, making source-capture extraction the most effective approach. Common features include:
Compact workstations (0.5–1 m height, fixed benches or jigs)
Varied welding methods (SMAW, GMAW, GTAW, occasional laser demonstrations)
Fluctuating usage (e.g., 19 booths active during exams vs. 3 during instructor demos)
Limited space (low ceilings of 3–4 m, minimal room for large equipment)
Budget-conscious needs (modular, expandable solutions preferred)
Since fumes disperse rapidly in confined areas, general ventilation alone fails to meet safety standards. A localized fume extraction system for welding school applications is the only reliable solution.

Designing an Effective Fume Extraction System for Schools
Two primary source-capture methods are used in welding schools: fume extraction arms and fume extraction hoods.
Hoods are typically mounted 2 meters above the floor, but this distance allows fumes to drift through the welder’s breathing zone before being captured. For optimal safety, fume extraction arms are the superior choice—positioned closer to the weld, they remove contaminants before they reach the student.
Key Design Considerations
Airflow Requirements:
1,200 m³/h per booth for student training
1,500 m³/h per booth when professionals use the space
Additional 10% capacity for ductwork (e.g., 60 m of 200 mm spiral duct with two 90° bends)
Noise Control:
Centrifugal fans should operate below 75 dB(A) to avoid disrupting instruction.
Scalability:
Modular filtration allows for easy expansion (e.g., adding three more booths without replacing the entire system).

(Fume Extraction Design Chart for Welding School)
Success Story: Yibin Xuanfeng Welding Center
After installing 19 extraction arms, 60 m of ducting, and a 24,000 m³/h dust collector, the center saw dramatic improvements:
Hexavalent chromium levels dropped from 18 µg/m³ to under 2 µg/m³ (OSHA’s permissible limit: 5 µg/m³).
Headache complaints decreased by 80%.
Local media praised the school’s safety commitment, leading to a 30% enrollment increase the following term.
Conclusion: A Must-Have for Modern Welding Schools
A high-performance fume extraction system for welding school environments is no longer optional—it’s a critical investment in student safety, regulatory compliance, and institutional reputation. By implementing scalable solutions like the LW12 series, schools can ensure clean air, meet standards, and support future growth.
Ready to upgrade your welding lab? Request a free airflow assessment today and discover how the LW12 series can transform your facility into a safer, more productive learning space.
You maybe like

Dric dust collection system is easy to install,and it occupies little space in your workshop.
For Large Welding Shops, Enclosed Working Zones
Easy to Install
High Cost-performance
Related Success Stories
Request Quote
Tell us your inquiry, we will recommend a suitable product model or solution for you!