-
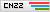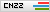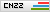
 COD
CODRemoval Rate:>97%
-
 Aniline
AnilineRemoval Rate:>99%
-
 Nitrobenzene
NitrobenzeneRemoval Rate:>98%
Introduction
The rubber manufacturing industry faces significant challenges in treating wastewater containing toxic organic pollutants such as cyclohexylamine, aniline, and nitrobenzene. This case study explores a high-efficiency rubber wastewater treatment project in China Cangzhou Lingang Economic & Technological Development Zone, where a 47,000-ton/year rubber additive production plant successfully implemented an advanced EPC industrial wastewater treatment system. By combining ozone pretreatment, A/O bio-enhanced process, and modified Fenton oxidation, the facility achieved stable discharge compliance with low operational costs.
Project Overview
Challenges in Rubber Additive Wastewater Treatment
The wastewater from rubber additive production contains:
High concentrations of COD (3,000–4,000 mg/L)
Aniline (~500 mg/L), nitrobenzene (~100 mg/L), and ammonia nitrogen (~300 mg/L)
Strong odor, deep color, and poor biodegradability
Conventional biological methods struggle to treat such complex wastewater effectively, necessitating an advanced chemical-biological combined process.
Wastewater Treatment Process Design
The EPC contractor adopted a three-stage treatment system:
Ozone Pretreatment – Breaks down refractory organics, reduces toxicity, and improves biodegradability.
A/O Bio-Enhanced Process – Utilizes specialized bacteria to degrade organic pollutants efficiently.
Modified Fenton Oxidation – Ensures final effluent compliance by removing residual COD and toxic substances.
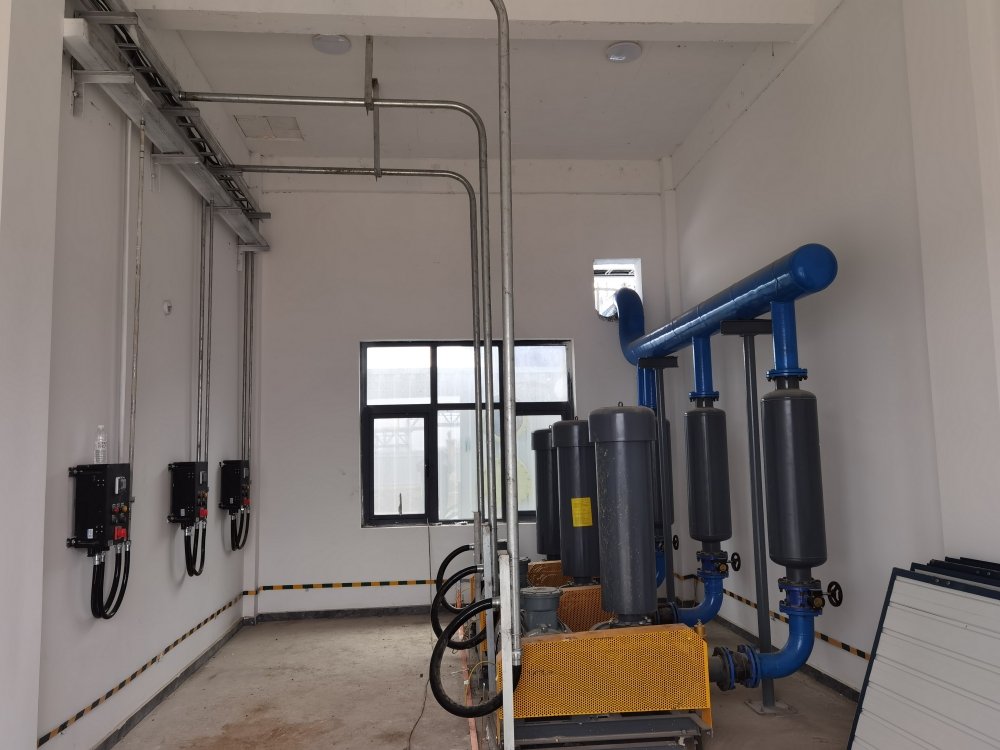

Innovative Construction: Prefabricated Enamel Tanks
To enhance corrosion resistance and reduce costs, the project used prefabricated enamel assembly tanks, offering:
Fast installation (30% shorter than traditional methods)
Strong corrosion resistance (ideal for chemical wastewater)
Compact footprint & cost savings
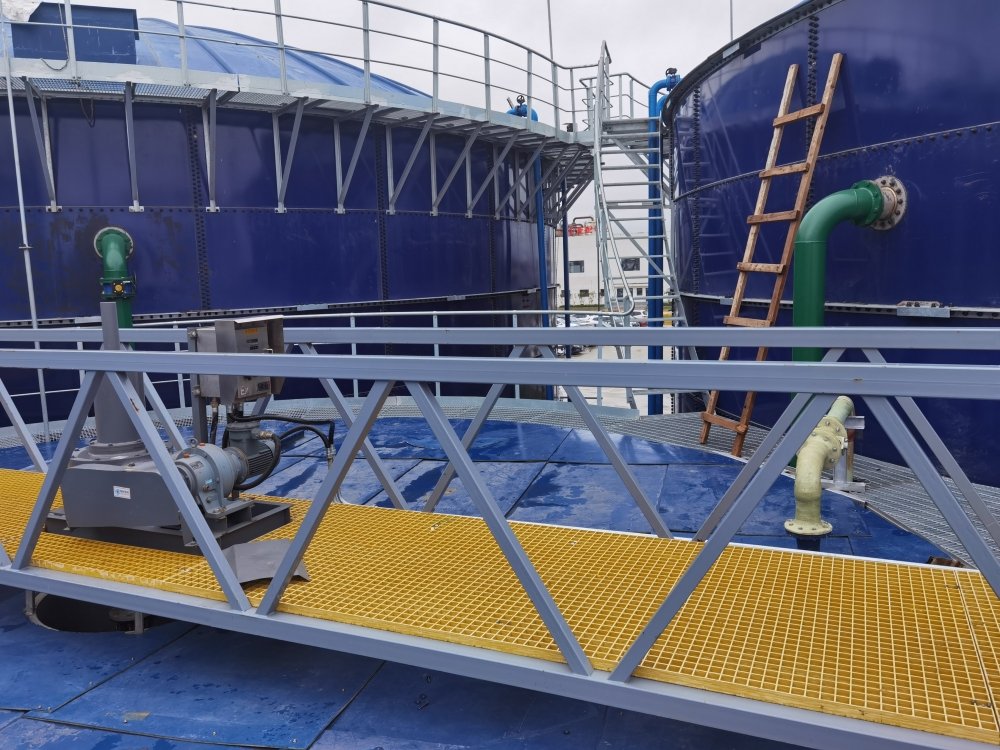

Treatment Performance & Cost Analysis
Effluent Quality (Meeting China Strict Standards)
| Parameter | Influent (mg/L) | Effluent (mg/L) | Removal Rate |
| COD | 3,000-4,000 | ≤80 | >97% |
| Aniline | ~500 | ≤1 | >99% |
| Nitrobenzene | ~100 | ≤2 | >98% |
| Ammonia Nitrogen | ~300 | ≤15 | >95% |
Operating Cost: Only $0.7/m³
The low treatment cost makes this solution highly sustainable for industrial applications.
Conclusion
This rubber additive wastewater treatment project demonstrates how ozone + Fenton oxidation + biological treatment can effectively handle high-toxicity industrial wastewater. With high removal rates, low costs, and compact design, this EPC wastewater treatment system is an ideal solution for chemical and rubber industries. For businesses seeking reliable industrial wastewater treatment technologies, this case offers valuable insights into sustainable and cost-effective pollution control. Contact us today, get free customized industrial wastewater treatment solution!
Request Quote
Tell us your inquiry, we will recommend a suitable product model or solution for you!